Jeff Bezos last week announced he will be stepping down from his role of CEO Amazon. Bezos is following Microsoft’s lead and putting his cloud executive Andy Jassy in charge of the company. Given that Microsoft was exceedingly successful with putting Satya Nadella in the same role, it would seem that this would be a slam-dunk success.
But the issue is that Amazon is not Microsoft; it is an online retail company with an unusual interest in cloud services. Amazon’s success is that, up until now, its cloud business was run by a subject matter expert, and Bezos, while building Amazon, became an expert in online retail.
Blue Origin, which Elon Musk’s SpaceX has significantly eclipsed, is also run by experts. Still, Bezos isn’t a rocket scientist, and this game of musical chairs will end with their cloud expert running the retail business and Bezos attempting to run full time a rocket company.
This effort will almost certainly not end well because each executive’s skills — with the possible exception of who takes over Andy Jassy’s cloud job — are unqualified for the part of Bezo’s empire they are running.
Let’s explore this potential train wreck this week, and we’ll close with my product of the week, the new robotic Echo Show 10.
Succession
One of the most significant omissions with companies that are just a few decades old, like Amazon, is the lack of a formal succession training program for the CEO job.
Often the CEO founder, who has grown up with their company, doesn’t realize the unique skills they have and assumes almost any senior executive can do the job.
More mature companies like IBM have formal programs where employees are identified early and extensively trained as executive assistants by former CEOs, and in various company roles. Hence, they gain the breadth they need for the job that they can demonstrate to the board when it comes time to replace the CEO. Like I did when I was in the IBM program, they also learn whether they even want the job (I didn’t).
Why Bezos Is Likely Leaving
This lack of formal succession often results in the selected CEO underperforming because they either lack the necessary breadth or the interest to do the job as it needs to be done. The typical reason that a CEO like Bezos voluntarily steps down is that they no longer enjoy the job, which becomes very political, bureaucratic, and increasingly regulated as the company grows.
Amazon is facing a vast number of things that I’m sure most of us wouldn’t enjoy facing any more than Jeff Bezos does. The company is being unionized, is under antitrust review, its taxes are about to go up a lot, and it faces increasing competition from Walmart and China’s online retail firms.
Because of Amazon’s size, it’s restricted from many aggressive ways to compete. Both the unionization effort and antitrust investigation could result in massive headaches for the CEO.
Wrong Choice
Now, the guy that likes running a cloud business that isn’t facing antitrust and isn’t being unionized mostly requires technical competence rather than political savvy. Both union fighting and litigation experience don’t look like a fit to me.
When Microsoft pivoted to become a cloud business it was no longer under an antitrust cloud. As a result, competent technical leaders like Nadella and, a decade earlier, Steve Ballmer made more sense because Microsoft dealt with operational problems resulting from their antitrust effort. Even so, Balmer was still viewed as a failure because he lacked the technical competence needed to run a technology company.
Given the threats to, and the nature of, Amazon’s business, the company needs someone who understands how to address the threats and grasps the online retail market. Where Amazon needs its top cloud expert isn’t running the company; it’s running AWS, a mostly separate entity that also has Amazon as a client.
To offer an analogy, Amazon is doing this as if Microsoft and Walmart merged, and Satya Nadella ran the combined company. There is a pretty good chance that both Microsoft and Walmart would suffer, since Satya does not have the retail comprehensiveness to run Walmart.
I expect this move at Amazon to demonstrate that a successful CEO must be an expert in the business of the company, and also be able to formulate a strategy to address the imminent threats the firm faces.
A better move would have been to anticipate an unfavorable antitrust action and spin off AWS as a separate company to help ensure that result wouldn’t damage the company. As part of Amazon, selling cloud services to other retailers or into markets like China is problematic due to Amazon’s retail power.
Separately, Amazon would be free to compete against Microsoft and Google more evenly because it wouldn’t be seen as a competitor or threat to many companies. Businesses, as a general practice, avoid buying from competitors like the plague.
Repeating Bill Gates’ Mistake
When he went through the antitrust trials, Bill Gates realized he no longer enjoyed the job of running Microsoft. Things had changed a lot and became similar to what Bezos is facing at Amazon: assorted government challenges, bureaucracy, and people stopping you from doing things you enjoy.
Bill wanted out, and he saw running his charity as something he’d enjoy more. But rather than looking for the best candidate to replace him, he picked the easiest in Steve Ballmer. That cost the company one of their best operational executives and caused Gates the loss of his closest friend.
Even though there was supposed to be an overlap where Bill trained Steve, Bill pretty much moved on and left Steve to screw up — which Steve did with a vengeance. Most notable were the failed Yahoo acquisition, the Nokia acquisition, Windows Vista, Windows 8, and the Zune debacle.
It wasn’t that Ballmer was a lousy manager; he did impressively well until he became CEO, whereupon he was out of his depth, which in turn made him overly defensive, which led to him not getting timely help.
About that help: Bill did provide Steve with a technical resource out of Lotus’ Iris software group, but Ray Ozzie (who replaced Gates as chief architect) didn’t get along with Balmer, likely because Steve saw him as more of a threat than a partner. Also, Ray wasn’t known to work well in large companies and hadn’t grown up at Microsoft, making him a poor choice. They should have selected someone that Steve liked from inside Microsoft to offset his lack of programming skills and knowledge.
Bezos appears to be making this same mistake, choosing someone not because they have the right skills but because they are comfortable and foolish enough to take the job without realizing they are likely to hate it.
Back to the Microsoft-Walmart analogy…Think about it: If Satya Nadella were offered the job to run Walmart, even though he is a successful CEO, I think he’d be smart enough to say “hell no.” That situation would bring about all the stuff he hates about being CEO without any of the technical aspects he loves; and he’d have to learn large scale retail and how to manage unionized employees (Walmart has been fighting unions for years, mostly with surprising success).
Like Gates and Ballmer, Bezos and Jassy appear to be close friends, and just like with Gates and Ballmer, friendship is unlikely to survive this move if, as I expect, Jassy is now a square peg in a round hole.
Wrapping Up
Companies need succession planning. CEOs aren’t immortal; they aren’t infallible, they aren’t always honest, and they often have issues with abusing power, given that every CEO will need to be replaced at some point.
It is the board’s job to find the best person for the job. With good succession planning, the firm will have internally several viable candidates at any time that are trained and ready to step in. Without it, you get something like we saw at Microsoft with Steve Ballmer; and now see with what I view as a bad skills match that will likely damage Amazon and force out their top cloud executive, hence damaging AWS.
Unlike Bill Gates’ charity, running a rocket company will be problematic for someone that isn’t the right kind of engineer, much like running a software company was with Ballmer. There is always a chance this will work out, but the odds don’t look good and, I expect, Amazon, AWS, and Blue Origin will all be badly harmed by this move.

The Amazon Echo Show 10
I’m a colossal Echo fan. I’ve had nearly every Amazon Echo made since the firm came out with the platform. This digital assistant is our home’s music source, it helps manage our shopping and it even turns out our lights at night.
There’s an Echo in every room of my house, except for closets and pet rooms (I’m a bit worried about what would happen if my pets figured out how to use it). We have the old Echo Show in the kitchen and my office. It works fine in my office mostly because I never really use the display and only ask it questions or to update shopping lists.
But, in the kitchen, the display isn’t angled correctly to use it for cooking, or to watch videos while cooking. Touching the device when you are preparing food can mess it up and, during a pandemic, touching anything others may touch is problematic. It will show if someone is at the door because it connects to the door camera, but that does you little good if you can’t see the display.
The new Echo Show 10 adds a motorized screen that will rotate to face you when you need to see something without touching it. Not only is that a ton more fun to show off when you have folks over, but it is also much more convenient when you have to see what is on the screen and your hands are dirty, or you are across the room at the wrong angle.
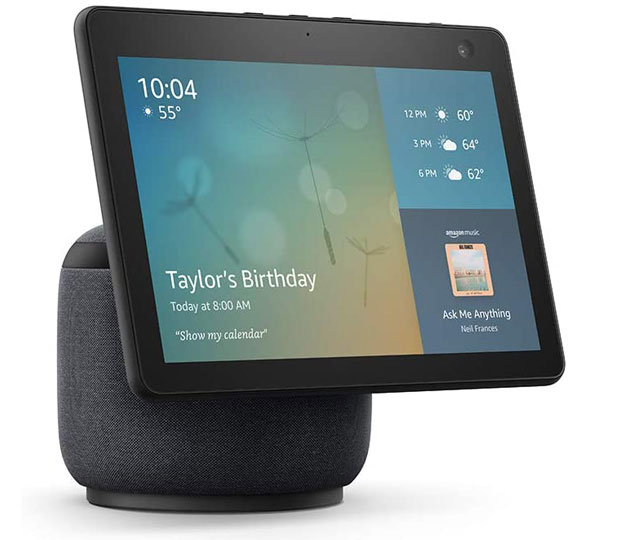

Ironically, it also looks like my favorite iMac — which for me is an added plus. The new Echo Show 10 will release on Feb. 25 for $249 — and it is my product of the week.